The world is just starting to get accustomed to Android Auto, and Google has already introduced an even newer technology. How is it different? And have we already tamed it?
Automotive OS: the rise of integrated intelligence

“I firmly believe that Automotive OS is the “next big thing” in the future of infotainment systems. It offers a ready-made system with all the benefits that Android has.”
– Jan Kučera, Division Director
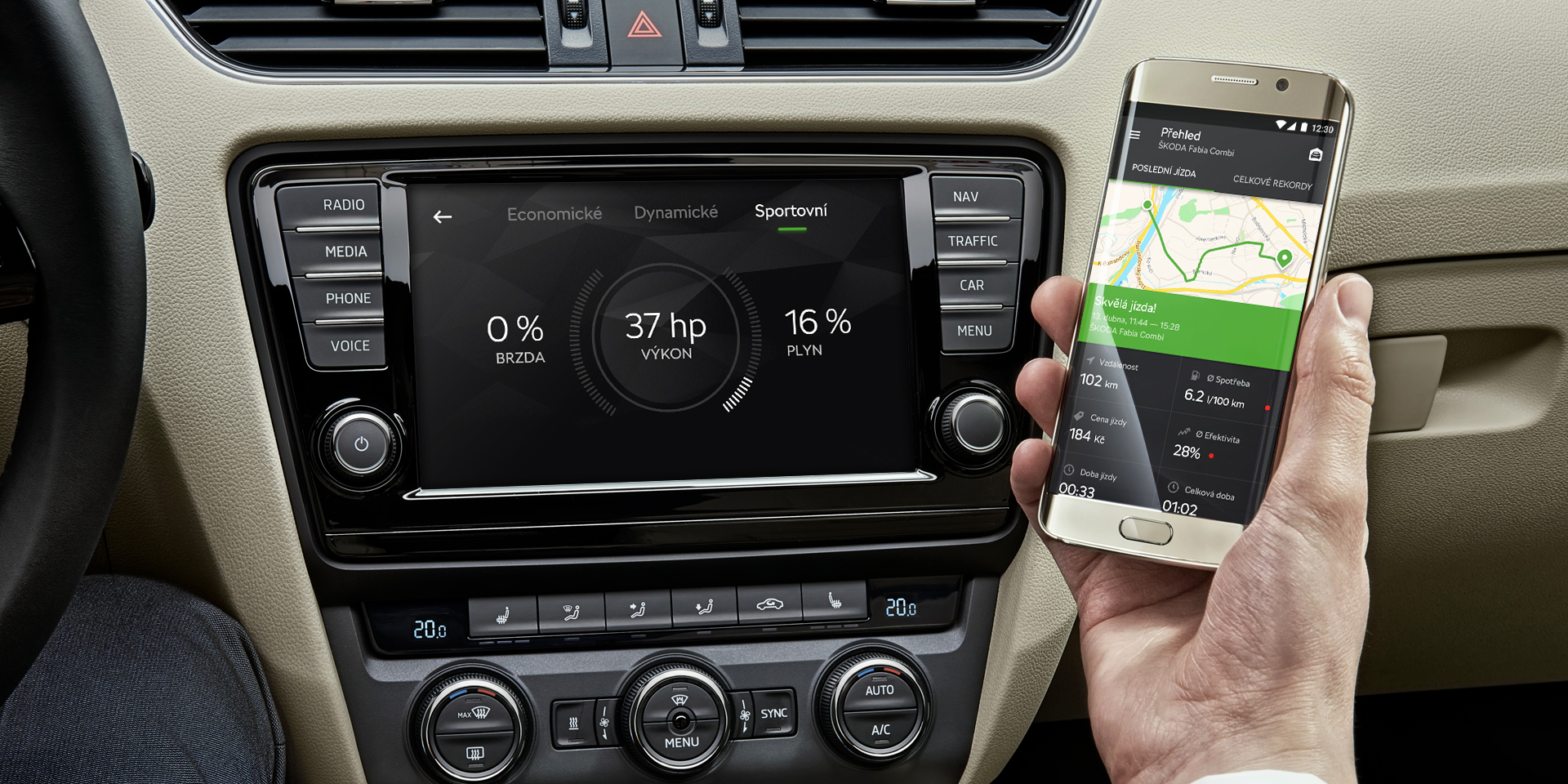
Android Auto has been making both the driver and passenger experience more pleasurable for over five years now. Basically, it offers voice control and easier access to GPS or music. Using this platform, we developed OneApp for Škoda. A solution that connects your smartphone with your car’s infotainment system and shows you all ride-related information. This app has won two prestigious prizes and its users are just plain happy. Nonetheless, we are looking to the future, and we know that the future is bigger than Android Auto and OneApp. Future? Not long ago, Google introduced its new system – Android Automotive OS.
How is this OS different? It doesn’t just mirror external applications on the infotainment screen. It connects the system to the car’s equipment, including seat heating or images from cameras around the car. The app itself runs within the infotainment, and all information and control panels are accessible from the big, built-in touchscreen, as well as from the display behind the steering wheel. This eliminates the need to have a smartphone with Android. It’s a stand-alone system that is also compatible with Apple. The OS is currently being used by Polestar 2 – a car made by Volvo, and the main competitor for Tesla. It goes to market this June, but we can already see the Automotive OS in action.
And the story doesn’t end there. Other manufacturers like General Motors have already signed a contract with Google, and cooperation with Audi, Mitsubishi, Nissan, and others is brewing. But the time when we’ll see cars cruising around and running this OS is still in the distant future. Yet, we’ve already started to develop our own system. It is true that there is basically no SDK available, so this phase can be summarized more as a playful learning process. But, thanks to our playfulness, we know we’ll be ready when the time comes.
If you are a technical person interested in our findings, here are our initial experiences. As you probably know – the Automotive industry is a very closed ecosystem. Full SDKs are accessible only to official partners and, outside of this environment, Google allows you to create only media player applications. Navigation and messaging apps creation will be allowed in the future. App development also must adhere to the new Android Automotive App Design Guidelines. The UI must meet the driver’s needs (large touch spaces and non-distractive experience). The Automotive OS often takes control over some operations (like playing music), so it’s mandatory to account for this when developing apps (the system stacks the activity in the best way to maintain ideal driving conditions, and therefore it’s not possible to have any Activity on the screen). The authorization is usually managed by connecting to a smartphone via Bluetooth or Google Sign In button. Another thing to keep in mind is the fact that there might be several drivers using one car, and user accounts will have to be switched. The first step of the actual development process is to set up the support of Automotive OS in Android Studio. Followed by running the emulator. Have a look at this guide from Google, it’s quite easy to follow.
Individual elements change their position and size automatically in order to make navigation in the app as easy as possible.
Thanks to our prototype, we already know that we can go a few steps beyond what’s officially offered, and we can collect data directly from the car. We simply can’t wait until we will be able to dig even deeper into this development process! And that’s coming soon…